construct the orbital diagram of each atom or ion.|6.4 Electronic Structure of Atoms (Electron Configurations) : Cebu What are Orbital Diagrams? Electron orbital diagrams are diagrams used to show the energy of electrons within the sublevels of an atom or atoms when used in bonding. .
Oiljoin.com has global traffic rank of 12,239,068. Oiljoin.com has an estimated worth of US$ 4,119, based on its estimated Ads revenue. Oiljoin.com receives approximately 250 unique visitors each day. Its web server is located in Singapore, with IP address 103.227.176.17. According to SiteAdvisor, oiljoin.com is unknown to visit.
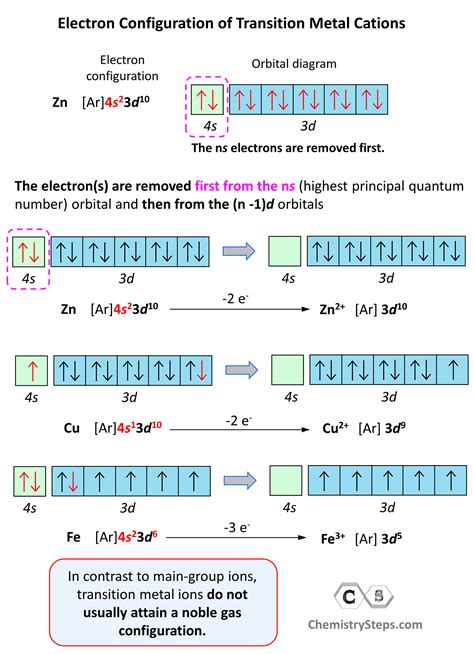
construct the orbital diagram of each atom or ion.,We will now construct the ground-state electron configuration and orbital diagram for a selection of atoms in the first and second periods of the periodic table.Commonly, the electron configuration is used to describe the orbitals of an atom .
Commonly, the electron configuration is used to describe the orbitals of an atom in its ground state, but it can also be used to represent an atom that has ionized into a cation .This free textbook is an OpenStax resource written to increase student access to high-quality, peer-reviewed learning materials.
construct the orbital diagram of each atom or ion. 6.4 Electronic Structure of Atoms (Electron Configurations)Equation 2.5.3 ml = −l, −l + 1,., 0,., l − 1, l. For example, if l = 0, ml can be only 0; if l = 1, ml can be −1, 0, or +1; and if l = 2, ml can be −2, −1, 0, +1, or +2. Each wave function .What are Orbital Diagrams? Electron orbital diagrams are diagrams used to show the energy of electrons within the sublevels of an atom or atoms when used in bonding. .The relative energy levels of atomic and molecular orbitals are typically shown in a molecular orbital diagram (Figure 8.34). For a diatomic molecule, t. What Is an Electron Orbital Diagram? Rules for Electron Orbital Charts. How to Draw Orbital Diagrams. Examples of How to Draw Electron Configuration. Lesson Summary. Frequently Asked.The periodic table can be divided into three categories based on the orbital in which the last electron to be added is placed: main group elements ( s and p orbitals), transition elements ( d orbitals), and inner transition .An orbital energy diagram is used to show the order in which electrons are assigned to energy levels. For the diagram below, label each energy level with the correct n .
For orbital diagrams, this means two arrows go in each box (representing two electrons in each orbital) and the arrows must point in opposite directions (representing paired spins). The electron configuration and .
For orbital diagrams, this means two arrows go in each box (representing two electrons in each orbital) and the arrows must point in opposite directions (representing paired spins). The electron configuration and orbital diagram of helium are: Figure 10.5f: Electron configuration and orbital diagram for helium (credit: Chemistry (OpenStax), CC .

Figure 2.5.8 Orbital Energy Level Diagram for the Hydrogen Atom Each box corresponds to one orbital. . each atomic orbital with a given set of quantum numbers has a particular energy associated with it, the orbital energy. In atoms or ions with only a . Orbitals in the Bohr model. Electrons fill orbit shells in a consistent order. Under standard conditions, atoms fill the inner shells (closer to the nucleus) first, often resulting in a variable number of electrons in the outermost shell.Hold up, I think this answer us lit It explains how to rock the orbital diagram for atoms or ions in a really organized way It takes you through determining the bumber of electrons figuring the electron config, drawing the prbital diagram, and assigning eGeneral Notes on Molecular Orbital Diagrams. The Y-axis of a MO diagram represents the total energy (not potential nor Gibbs Energy) of the orbitals. Individual atomic orbitals (AO) are arranged on the far left and far right of the diagram. Overlapping atomic orbitals produce molecular orbitals located in the middle of the diagram. The diagram shows the two atomic orbitals (AOs) that were used to generate the corresponding MOs. These are both \(1s\) orbitals, so these are shown at the extremes of the diagram as well as the electronic configurations of each atom. Here, just one electron occupies a single \(1s\) orbital. The two MOs generated from the two AOs . Molecular Orbital Diagrams. This scheme of bonding and antibonding orbitals is usually depicted by a molecular orbital diagram such as the one shown here for the dihydrogen ion H 2 +. Atomic valence electrons (shown in boxes on the left and right) fill the lower-energy molecular orbitals before the higher ones, just as is the case for .
Energy-Level Diagrams. Because electrons in the σ 1 s orbital interact simultaneously with both nuclei, they have a lower energy than electrons that interact with only one nucleus. This means that the σ 1 s molecular orbital has a lower energy than either of the hydrogen 1s atomic orbitals. Conversely, electrons in the \( \sigma _{1s}^{\star } \) orbital interact .construct the orbital diagram of each atom or ion. Atomic orbitals alone do not work for Molecules. Consider how we might explain the bonding in a compound of divalent beryllium, such as beryllium hydride, BeH 2.The beryllium atom, with only four electrons, has a configuration of 1s 2 2s 2.Note that the two electrons in the 2s orbital have opposite spins and constitute a stable pair that has .The valence molecular orbitals in both atoms are the \(2s\) and \(2p\) orbitals. The molecular orbital diagram for carbon monoxide (Figure \(\PageIndex{1}\)) is constructed in a way similar to how you would construct dicarbon or dioxygen, except that the oxygen orbitals have a lower potential energy than analogous carbon orbitals.

Here are electron shell atom diagrams for the elements, ordered by increasing atomic number. For each electron shell atom diagram, the element symbol is listed in the nucleus. The electron .We illustrate how to use these points by constructing a molecular orbital energy-level diagram for F 2.We use the diagram in part (a) in Figure \(\PageIndex{1}\); the n = 1 orbitals (σ 1 s and σ 1 s *) are located well below those of the n = 2 level and are not shown. As illustrated in the diagram, the σ 2 s and σ 2 s * molecular orbitals are much . There are two types of cobalt ions. The cobalt atom exhibits Co 2+ and Co 3+ ions. The cobalt atom donates two electrons in the 4s orbital to form a cobalt ion(Co 2+). Co – 2e – → Co 2+ Here, the electron configuration of cobalt ion(Co 2+) is 1s 2 2s 2 2p 6 3s 2 3p 6 3d 7. The cobalt atom donates two electrons in the 4s orbital and an .
It describes how electrons are distributed among the various atomic orbitals and energy levels, and provides a detailed map of where each electron is likely to be found. Fluorine is the 9th element in the periodic table and the symbol is ‘F’. The atomic number of fluorine is 9, which means its atom has nine electrons outside the nucleus.Assigning Electron Configuration . We write electronic configurations by following the aufbau principle (from German, meaning “building up”). First we determine the number of electrons in the atom; then we add electrons one at a time to the lowest-energy orbital available without violating the Pauli Exclusion Principle .That is, recognizing that each . NO is made up of one atom of nitrogen (N) and one oxygen (O) atom. The electronic configuration of a N-atom is 1s 2 2s 2 2p 3.. The electronic configuration of an O-atom is 1s 2 2s 2 2p 4.. 7 electrons of nitrogen and 8 electrons of oxygen make a total of 7 + 8 = 15 electrons available to be filled in the Molecular orbital diagram of the NO .Identify and count the pendant atoms' valence orbitals. Each of the three pendant hydrogen atoms has one valence orbital; the \(1s\). Thus, we can expect a total of three SALCs from these three atoms. . and then construct the molecular orbital diagram. The nitrogen \(2s\) orbital is about 12 eV lower in energy than a H \(1s\). This difference .
construct the orbital diagram of each atom or ion.|6.4 Electronic Structure of Atoms (Electron Configurations)
PH0 · The orbital diagram of each atom or ion. Construct Energy.
PH1 · Orbital Diagrams
PH2 · Electron Orbital Diagrams
PH3 · Chapter 2.5: Atomic Orbitals and Their Energies
PH4 · 8.4 Molecular Orbital Theory
PH5 · 8.4 Electronic Structure of Atoms – Introduction to
PH6 · 6.4 Electronic Structure of Atoms (Electron Configurations)
PH7 · 3.4: Electronic Structure of Atoms (Electron Configurations)
PH8 · 1.4: Electron Configurations and Electronic Orbital Diagrams